Autumn Gear Guide
Find inspiration in our Gear Guide that will keep you out on your bike through wind or rain.
Download NowFinding the perfect lock for your perfect bike
You’ve searched high and low and done your research. It took months of planning, but you finally made your decision – you’ve found your forever bicycle.
Then comes panic. It is no secret that most bicycle owners know their bicycle happiness can be quickly diminished by the underlying fear of bike theft. Many people know of at least one friend who experienced the loss of their ride, if they haven’t had one stolen first-hand. It is a worry that hangs over many purchase decisions, not only of the bicycle itself, but also the lock.
Thankfully, there are many options out there for all different types of riders. ABUS Mobile Security helps reduce the stress of decision making by offering a lock for all types of owners. Providing varying levels of security allows them to meet the needs and wants of each and every individual.
To help make the lock choice easier, here is a little matchmaking 101 to pick the perfect lock for your forever bike!
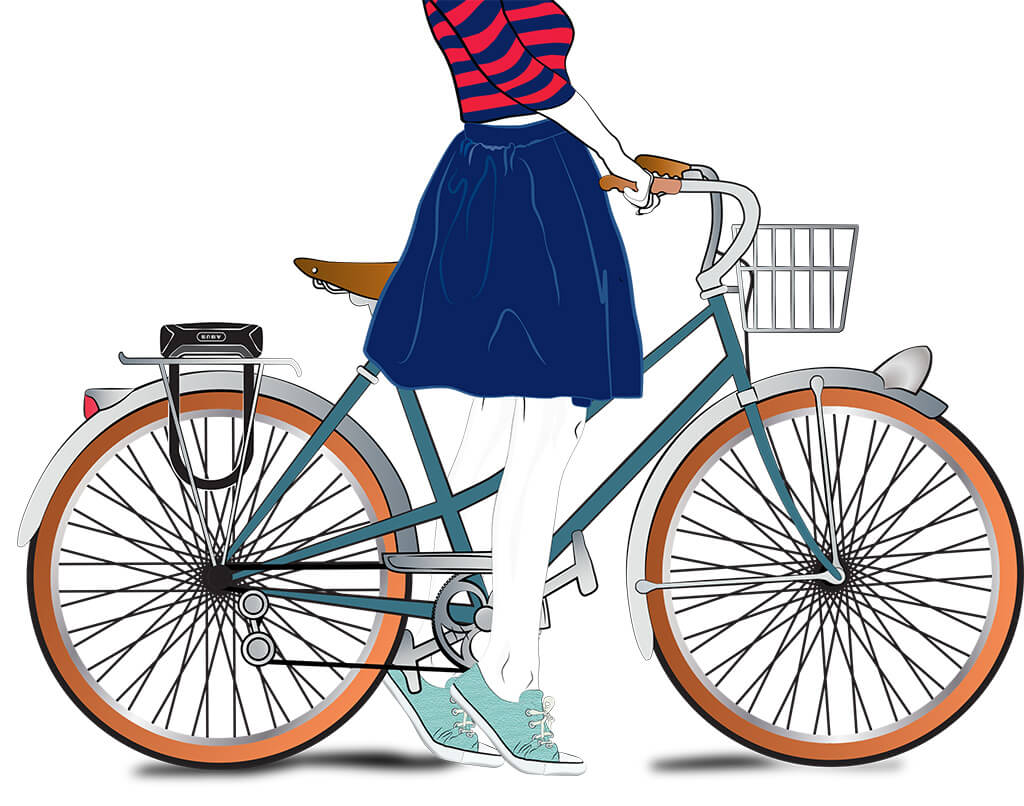

Spending a quiet night at home is not your style. Hopping from café, to restaurant and party with friends, your favorite way to travel is on your carefully sought-after vintage bicycle. Your ride is an extension of your fashionable style, and every accessory has to be just as special. The ABUS U-lock GRANIT Plus 640 is the perfect little lock to compliment your bike style. It’s sleek and simple, and easily attaches to your back rack for quick pick up and go. No need to fuss with a combination, the key lock makes it easy to grab and go, so you’ll only be fashionably late for your next event.
Security Level: 12
Mounting: TexKF – Bracket with textile strap, especially suitable for non-round frame profile with a diameter of 21-80 mm
Specs: Weight: 900g (31.75oz) Height: 230mm (9in) Width: 83mm (3.25in) Diameter: 12mm (0.5in)
Special Features: The shackle, case, as well as supporting elements of the locking mechanism are made of special hardened steel. Very intensive use of special weight-optimized alloy and light material.
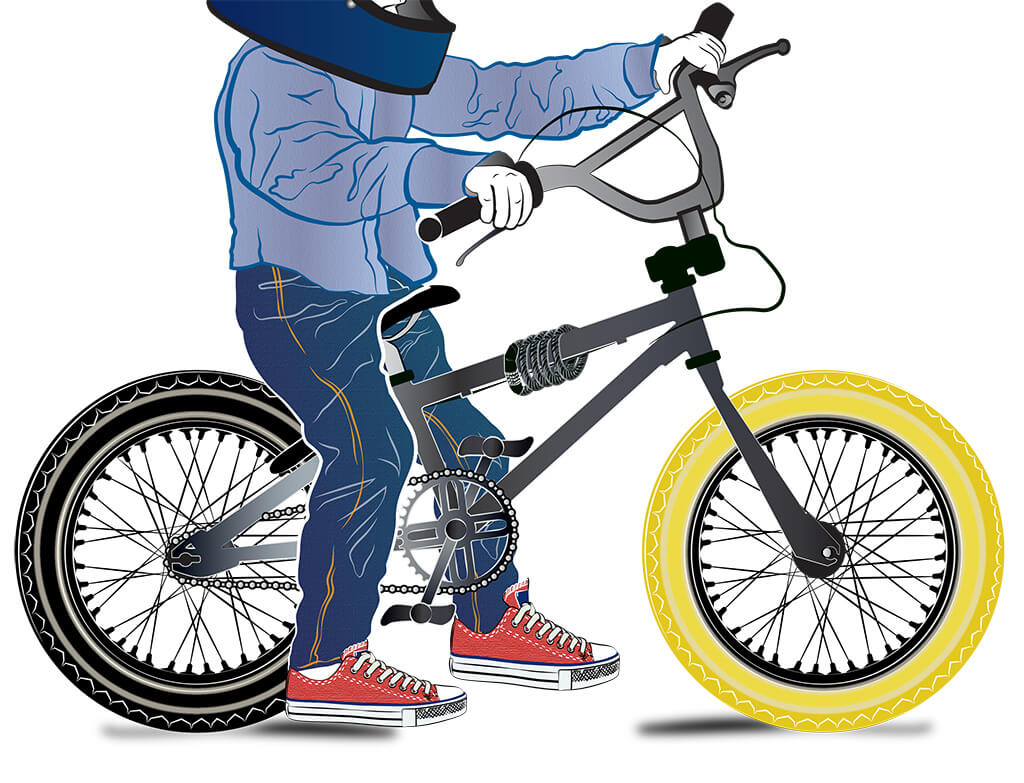

The day you first rode on your own was the day the world opened up, and it’s been hard to keep still since. You’re a kid on a mission, and age doesn’t hold you back from getting out and exploring. Sometimes, though, kids will be kids, and keeping your little bike safe while you’re focusing in the classroom has to be easy. The ABUS Numero 1300 Kids coil cable lock is ideal for your little hands. The springy coil means lots of stretch to wrap securely around your bike. The combination lock also means never having to explain to mom how you lost the key.
Security Level: 2
Mounting: Quick and easy. Simply wraps around the seat post for convenient storage while riding.
Specs: Weight: 314g (11oz) Width: 10mm (3/8in) Length: 1500mm (59.1in)
Special Features: Available in four colors (including black) to match any child’s bike
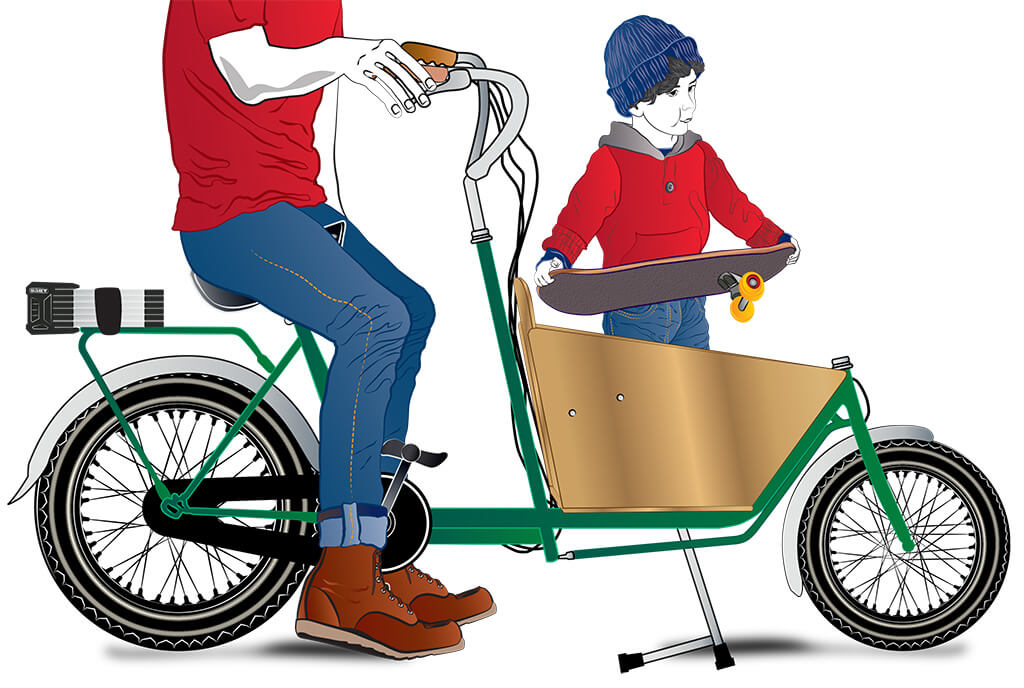

Having kids hasn’t changed your outlook on life, just how you get around with those kids. The day you found out you were going to be a parent, the research began, discovering the many ways families conveniently get around by bicycle. All that planning was rewarded with a beautiful cargo bike – the perfect way to get around with children, and still so practical for doing those larger grocery shopping trips without having to sacrifice your everyday cycling lifestyle. The family “vehicle” needs a very special lock, and the ABUS Bordo GRANIT X Plus 6500 folding lock certainly fits the bill. The most secure lock available, you can run your daily trips knowing the bike is safe, and it folds away discreetly, leaving lots of space for your precious cargo – a growing family.
Security Level: 15
Mounting: Flexible mounting with non-slip velcro straps to easily attach to frame, basket or seat post. Option to also screw into the bottle holder device.
Specs: Weight: 1580g (55.75oz) Circumference: 850mm (33.5in)
Special Features: ABUS Link-Protection-Shield offers high saw protection of the links. The bars, the links, the case as well as supporting elements of the locking system are made of special hardened steel.
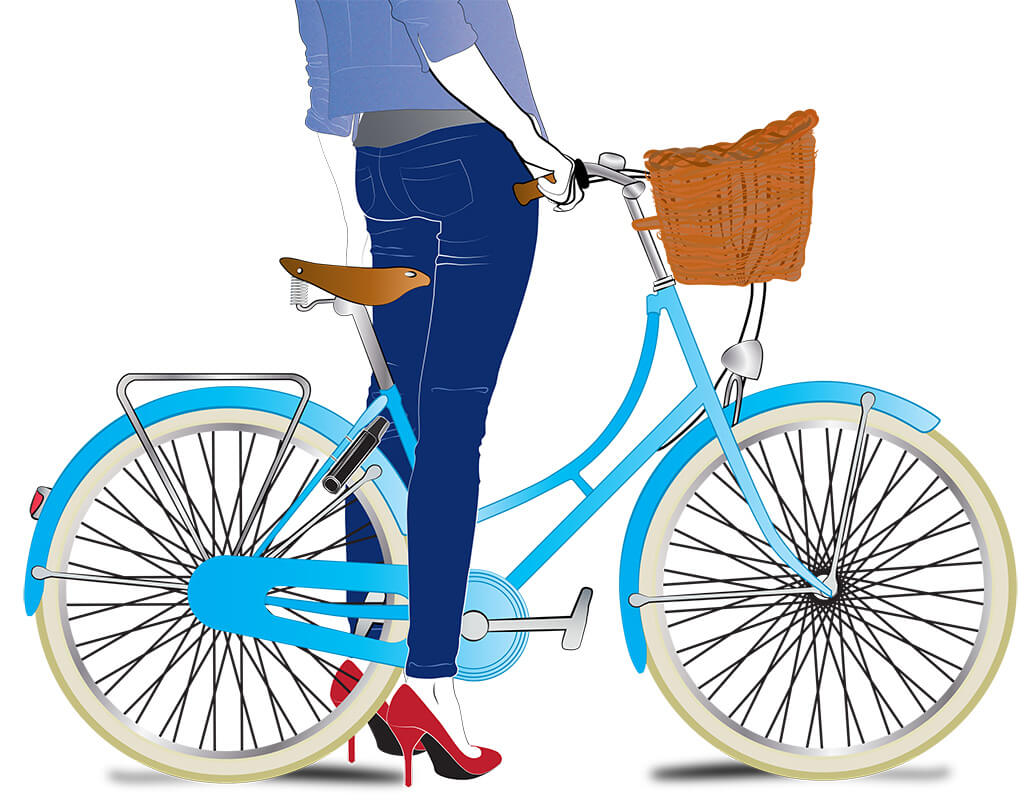

When you ride, you ride in style. Your beautiful Dutch style bike gets noticed every time you ride around town, evidence that your patience and investment have paid off. Although your look takes time, getting around town has to be easy and low-maintenance. Whether it is a trip to an important meeting, or just a quick jaunt to a local café for coffee with that special someone, each voyage is significant, and everything else needs to be stress-free. The ABUS Amparo 4850 frame lock makes locking up your gorgeous ride as simple as turning a key – literally! Awkwardly wrapping a greasy cable around your bike is a thing of the past. This lock immobilizes your wheel and when your stop will take a little more time, the added chain helps you rest assured that your dream bike will be there when you get back.
Security Level: 9 – increased through use of 4850 Chain or Cable
Mounting: Easy screwing or threading to rear frame. Cable or Coil easily transported with carrying bag.
Specs: Lock Weight: 770g (27.16oz) Height: 108mm (4.25in) Width: 63mm (2.5in) Diameter: 8.5mm (0.33in)
Chain Weight: 803g (28.3oz) Length: 60mm (2.3in) Circumference: 850mm (33.5in)
Cable Weight: 803g (28.3oz) Length: 1000mm (39.4in) Diameter: 6mm (0.25in)
Special Features: ABUS push’n lock, the patented closing mechanism, makes attachment of the accessory easy. Extra large aperture makes it adaptable to many wheel widths.
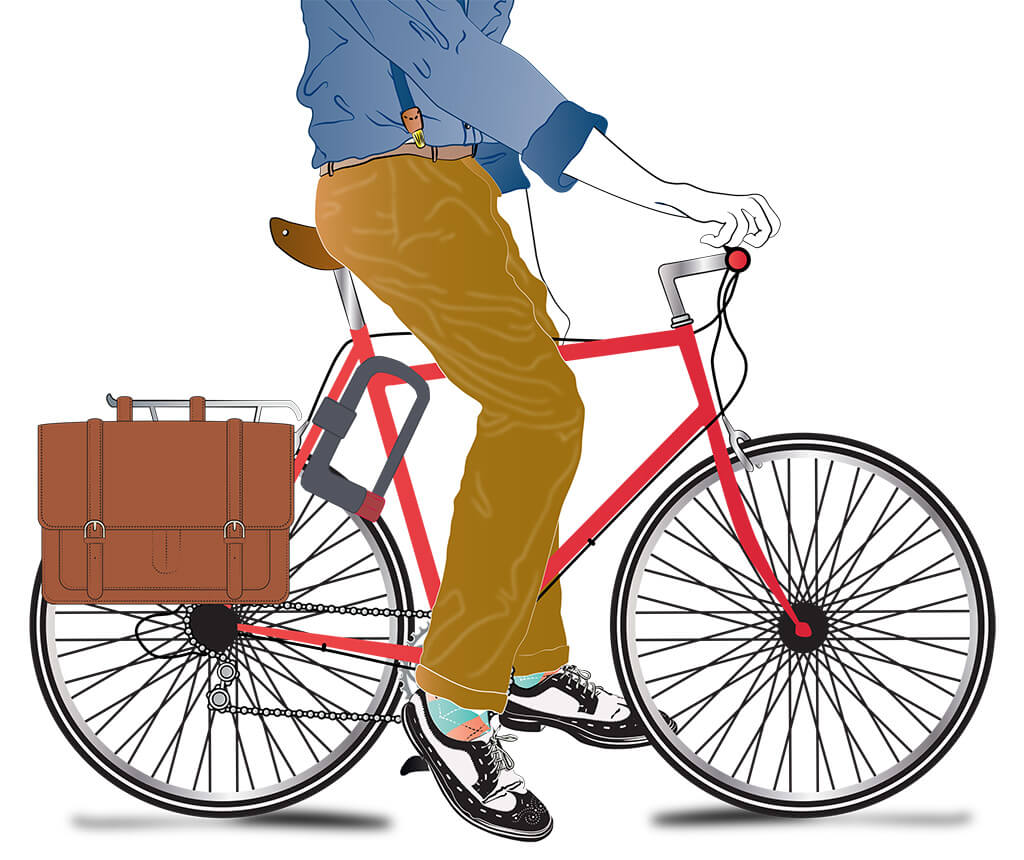

All that hard work day in and day out is worth it when you hop on the saddle of the bike you’ve spent months saving for. All the worries and stresses of the day melt away as you make the long commute home, tucking your suit jacket and tie into your pannier and letting loose. It took time to find the perfect hybrid commuter to get you to the office without having to resort to changing once you get there. Days are filled with high-level meetings and deals, but you value your home time too much to leave home early so you can freshen up when you arrive. Luck didn’t help you find your forever bike, and luck will not keep it safe when you’re working late to meet a deadline. The ABUS U-Grip Plus 501 u-lock ensures you have the best security possible, giving you one less thing to stress about throughout the day. After an extra long day, knowing your ride is waiting to take you away is the best feeling in the world.
Security Level: 13
Mounting: USH 501 – Universal bracket with easy mounting on round frames with a diameter of 15-35 mm
Specs: Weight: 1650g (58.2oz) Height: 225mm (8.9in) Width: 95mm (3.75in) Diameter: 13mm (0.5in)
Special Features: ABUS power cell technology (patented) offers the highest protection against hitting and pulling attacks. The shackle, case and supporting elements of the locking mechanism are made of special hardened steel.
For you, life is too short to spend it stressing the little things. The perfect day is spent cruising around the city and meeting up with friends at the beach to chill and watch the sunset. You’ve known from the start that the perfect bicycle was a simple beach cruiser – no fuss, low maintenance, and matching your relaxed outlook on life. Locking it up should not be complicated either, so the ABUS Iven Steel-O-Flex 8200 lock is exactly what you were looking for. As easy to use as a traditional cable, but more secure, it is a lock as laid back as you are. After all, “Life’s a beach,” and that’s where your friends can find you and your bicycle.
Security Level: 8
Mounting: UGH 02 – Universal bracket for the rack with a diameter of the struts of 5-16.5 mm
Specs: Weight: 1362g (48oz) Length: 850mm (33.5in) Diameter: 25mm (1in)
Special Features: The steel shells, case as well as supporting elements of the locking mechanism are made of special hardened steel. Due to the steel shells, the Steel-O-Flex locks reach a significantly higher security than common cable locks, yet maintain high flexibility (Double Protection).
No two bikes are created equal, and every rider spends time researching, test riding and selecting the perfect bike for them. When you find your forever bicycle, the thought of losing it should never overshadow the joy felt when riding it. That’s why matching it up with the best lock to suit your lifestyle is so important. Whether you need something quick and easy, or the highest security available, companies like ABUS offer so many options that matching a rider and their bike with the best lock for them is a cinch. Enjoy the freedom of two-wheeled travel knowing your bicycle will always be there, waiting for the next adventure.
ABUS has made selecting the right lock for your security needs easy with their simple-to-use grading system. The scale is based on the security level of the lock, and works on a scale of 1-15, with 1 being the lowest level of security. The system has been developed with the consumer in mind, and is a clear and easy graphic representation.
Security Levels 1-4: These locks provide basic protection, and are best suited for use in low risk areas for theft. Most times, these locks are used for children’s bikes, or as a secondary lock, or for securing accessories like saddles and helmets.
Security Levels 5-9: Locks in this range are perfect for entry level adult bikes, and for use in low to medium theft risk areas. For better security, it is also recommended for use as a secondary lock.
Security Levels 10-15: Locks in this range provide the maximum level of security, and are recommended for bicycles with higher value, locking in urban neighborhoods or areas of high theft risk. Level 15 is represented by a completely red dial, making it easy to identify the highest level of protection.
Find inspiration in our Gear Guide that will keep you out on your bike through wind or rain.
Download Now
Hi Chris & Melissa,
Thanks for sharing such an informative content. It helped me choosing the best bike lock that satisfies my needs. I was searching for the past few days to get the best lock for my bike but couldn’t find any useful content. Today I landed up on your page accidentally and it really helped me. Hats off for the great work.
Comments are closed.